With the improvement of consumers’ health awareness, traditional sweeteners represented by aspartame, acesulfame potassium, sucralose, etc. are being abandoned by consumers. Low-sugar and sugar-free products are beginning to become mainstream trends in the market. Consumer demand for natural, safe and healthy products is driving the market for natural sweeteners such as stevia, erythritol, and allulose. However, they still have some shortcomings, such as post-bitterness and sweetness that are not as strong as sucrose, and other ingredients are required to be compounded.
In recent years, the sugar substitute raw material product market has been homogenized, and the overall market competition is relatively scattered. Some companies set their sights on “sweet protein”. According to the existing data research, there are many kinds of sweet proteins in nature, but this raw material has not been as popular in the market as sweeteners such as stevia and erythritol for a long time and has not been fully developed. The more typical sweet proteins are miracle fruit, Brazil sweet protein, curculin, capersin and so on.
1 “Mystery Fruit” has been awarded the EU’s new resource food status
Recently, the European Commission issued Regulation (EU) No. 2015/2283. In accordance with Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 of the European Parliament and of the Council and the revised Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2017/2470, the marketing of the dried fruit of the miracle fruit (Synsepalum dulcificum) as a new resource food is approved.
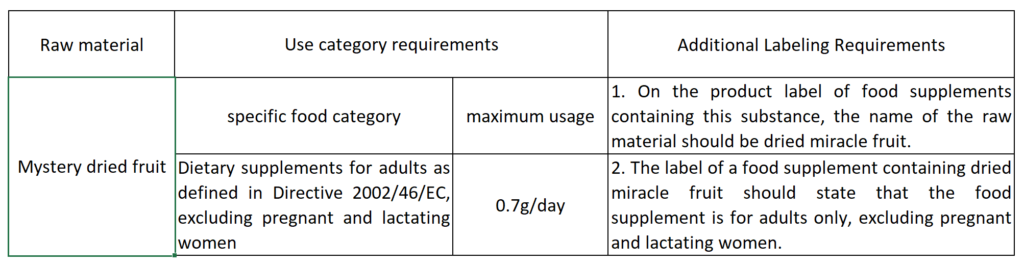
As early as November 14, 2018, Medicinal Gardens S.L. submitted an application to the European Commission pursuant to Article 10(1) of Regulation (EU) 2015/2283, requesting that dried miracle fruit be placed in the EU as a new resource of food market. At the same time, the product can be used in the category of food supplements, with a maximum daily intake of 0.7 grams, and the target group is general adults, except for pregnant and lactating women.
In terms of specific applications, please refer to the use requirements of the European Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2017/2470 for details. The details are as follows:
2 The magic protein that makes sour sweet
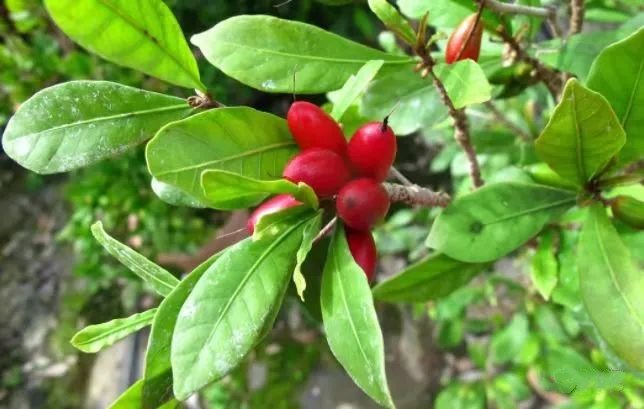
Miracle fruit is a perennial evergreen shrub belonging to the genus Miracle of the genus Mirage. The fruit is a single fruit, oval, bright red when ripe. It is quite mysterious because of its unique taste-changing function. It is a kind of plant that combines fun, ornamental, and edible properties. This fruit is native to Ghana and Congo in West Africa and was introduced to southern China in the 1960s. It is traditionally eaten before other fruits such as citrus, or before foods and drinks made from sour palm.
Miracle fruit pulp contains a substance called miracle fruit protein, which is a natural taste modifier that temporarily converts sourness into sweetness. In 1968, a Japanese scientist at Florida State University, Awahara Kenzo, extracted and isolated this substance (Miraculin) from the miracle fruit, and published the results in the journal “Science”. The door to taste.
Miracle protein is a unique glycoprotein found in the pulp of berries that binds to sweet taste receptors (HT1R2 and HT1R3) on the human tongue. It turns into a sweetness inducer when it encounters sourness, which is not inherently sweet and will sweeten sour foods and drinks. However, the question of how miraculin allows taste buds to make taste modifications remains unexplained.
However, it should be noted that only in acid conditions, the magic fruit protein can activate sweet taste receptors, so after eating this kind of thing, eating sweets will not feel sweet. Only if you eat sour food, you will feel sweet.

3 Market application potential of the product
Miracle fruit is a low-calorie ingredient that is also rich in antioxidant polyphenols and vitamin C. At present, the raw material can be applied in specific fields, such as taste management, diabetes, weight control. In the field of nutrition, it can act as a natural taste modifier, changing consumers’ dietary perceptions. In terms of specific food and beverages, it can be used in ice cream, fruit juice, popsicles, functional foods, snacks, chewing gum, etc.
In terms of specific product applications, dysgeusia is a potential direction. About 5% of people suffer from dysgeusia, with a prevalence of 56-76% in certain medical conditions. Dysgeusia affects consumers’ quality of life, causing malnutrition and reducing life expectancy.
Weight management is also a promising direction. About 40% of adults are overweight, of which 15% are obese. This is a chronic disease. This sweet protein can help people reduce sugar cravings, promote satiety, and avoid consuming artificial sweeteners that alter microbes. Thus, by improving the palatability of low-carb foods, increasing adherence to a weight management diet.

